Personal Blackbox (pbb.me) is a new #VRM company — or so I gather, based on what they say they offer to users: “CONTROL YOUR DATA & UNLOCK ITS VALUE.”
So you’ll find them listed now on our developers list.
Here is the rest of the text on their index page:
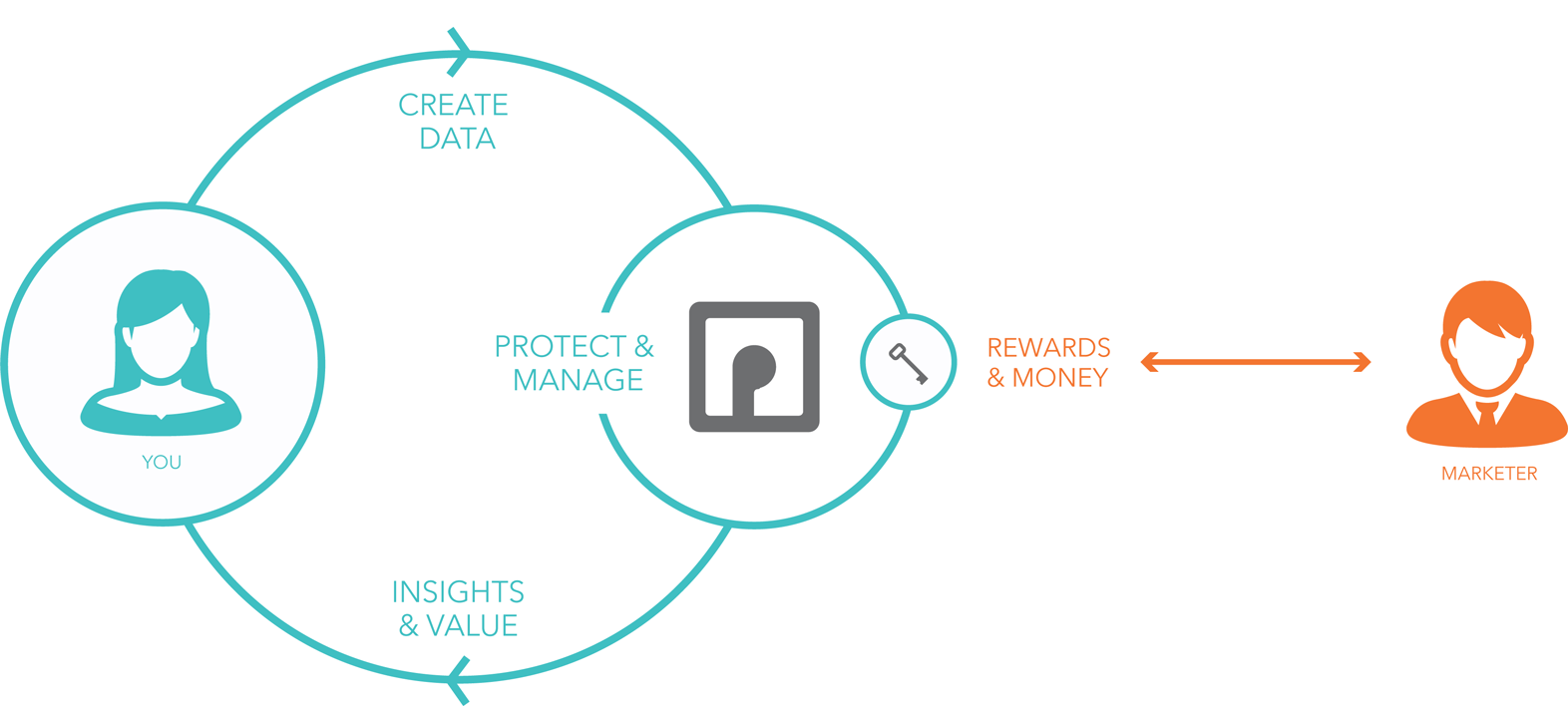
PBB is a technology platform that gives you control of the data you produce every day.
PBB lets you gain insights into your own behaviors, and make money when you choose to give companies access to your data. The result? A new and meaningful relationship between you and your brands.
At PBB, we believe people have a right to own their data and unlock its benefits without loss of privacy, control and value. That’s why we created the Personal Data Independence Trust. Take a look and learn more about how you can own your data and its benefits.
In the meantime we are hard at work to provide you a service and a company that will make a difference. Join us to participate and we will keep you posted when we are ready to launch.
That graphic, and what seems to be said between the lines, tells me Personal Blackbox’s customers are marketers, not users. And, as we so often hear, “If the service is free, you’re the product being sold.”
But, between the last paragraph and this one, I ran into Patrick Deegan, the Chief Technology Officer of Personal Blackbox, at the PDNYC meetup. When I asked him if the company’s customers are marketers, he said no — and that PBB (as it’s known) is doing something much different that’s not fully explained by the graphic and text above, and is tied with the Personal Data Independence Trust, about which not much is said at the link to it. (At least not yet. Keep checking back.) So I’ll withhold judgement about it until I know more, and instead pivot to the subject of VRM business models, which that graphic brings up for me.
I see two broad ones, which I’ll call vault and honey pot.
The vault model gives the individual full control over their personal data and what’s done with it, which could be anything, for any purpose. That data primarily has use value rather than sale value.
The honey pot model also gives the individual control over their personal data, but mostly toward providing a way to derive sale value for that data (or something similar, such as bargains and offers from marketers).
The context for the vault model is the individual’s whole life, and selective sharing of data with others.
The context for the honey pot model is the marketplace for qualified leads.
The vault model goes after the whole world of individuals. Being customers, or consumers, is just one of the many roles we play in that world. Who we are and what we do — embodied in our data — is infinitely larger that what’s valuable to marketers. But there’s not much money in that yet.
But there is in the honey pot model, at least for now. Simply put, the path to market success is a lot faster in the short run if you find new ways to help sellers sell. $zillions are being spent on that, all the time. (Just look at the advertising coming along with that last link, to a search).
FWIW, I think the heart of VRM is in the vault model. But we have a big tent here, and many paths to explore. (And many metaphors to mix.)

 In
In