Check the Arbitron radio listening ratings for Washington DC. You have to go waaaay down the list before you find a single AM station that isn’t also simulcast on FM. But then, if you go to the bottom of the list, you’ll also find a clump of Internet streams of local radio stations.
You’ll see the same pattern at other cities on this list from Radio-Info.com. FM on top, AM below, and streams at the bottom.
Together these paint an interesting picture. At the top, Innovators, at the bottom, Dilemma. (Some context, if the distinction isn’t obvious.)
Note that Pandora, Spotify, SiriusXM and other radio-like streaming services are not listed. Nor are podcasts or anything else one might listen to, including stuff on one’s smartphone, ‘pod or ‘pad. If they were, they’d be way up that list. According to Pandora CEO Joseph Kennedy (in this Radio INK piece),
…we have transitioned from being a small to medium sized radio station in every market in the U.S. to one of the largest radio stations in every market in the country. Based on the growth we continue to see, we anticipate that by the end of this year, we will be larger than the largest FM or AM radio station in most markets in U.S. As a consequence, our relevance to buyers of traditional radio advertising in skyrocketing. We have already begun to see the early benefits of this dramatic change. Our audio advertising more than doubled to more than $100 million in fiscal 2012.
Back when I was in the biz, public radio was a similar form of dark matter in the ratings. If you added up all the stations’ shares, they came 10-13% short of 100%. If one went to Arbitron’s headquarters in Beltsville, Maryland (as many of us did) to look at the “diaries” of surveyed listeners, you’d find that most of the missing numbers were from noncommercial stations. Today those are listed, and the biggest are usually at or near the top of the ratings.
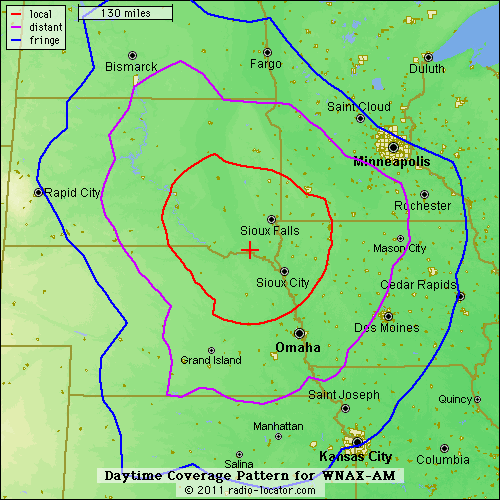
But today’s dark matter includes a variety of radio-like and non-radio listening choices, including podcasts, satellite radio, and what the industry calls “pure-play streamers” and “on-demand music services.” Together all of these are putting a huge squeeze on radio as we knew it. AM is still around, and will last longest in places where it’s still the best way to listen, especially in cars. In flat prairie states with high ground conductivity, an AM station’s signal can spread over enormous areas. For example, here is the daytime coverage map from Radio-Locator.com for 5000-watt WNAX/570am in Yankton, South Dakota:
And here’s the one for 50000-watt WBAP/820 in Dallas-Fort Worth:
No FM station can achieve the same range, and much of that flat rural territory isn’t covered by cellular systems, a primary distribution system for the data streams that comprise Internet radio.
True, satellite radio covers the whole country, but there are no local or regional radio stations on SiriusXM, the only company in the satellite radio business. To some degree rural places are also served by AM radio at night, when signals bounce off the ionosphere, and a few big stations — especially those on “clear” channels — can be heard reliably up to several thousand miles away. (Listen to good car radio at night in Hawaii and you’ll still hear many AM stations from North America.) But, starting in 1980, “clears” were only protected to 750 miles from their transmitters, and many new stations came on the air to fill in “holes” that really weren’t. As a result AM listening at night is a noisy mess on nearly every channel, once you move outside any local station’s immediate coverage area on the ground.
Even in Dallas-Fort Worth, where WBAP is the biggest signal in town (reaching from Kansas to the Gulf of Mexico, as you see above), WBAP is pretty far down in the ratings. (Copyright restrictions prevent direct quoting of ratings numbers, but at least we can link to them.) Same for KLIF and KRLD, two other AM powerhouses with coverage comparable to WBAP’s. News and sports, the last two staple offerings on the AM band, have also been migrating to FM. Many large AM news and sports stations in major metro areas now simulcast on FM, and some sound like they’re about to abandon their AM facilities entirely.WEEI in Boston no longer even mentions the fact that they’re on 850 on the AM dial. Their biggest competitor, WBZ-FM (“The Sports Hub”) is FM-only.
But while FM is finally beating AM, its ratings today look like AM’s back in the 1950s. FM wasn’t taken seriously by the radio industry then, even though it sounded much better, and also came in stereo. Today the over-the-air radio industry knows it is mightily threatened (as well as augmented, in some cases) by streaming and other listening choices. It also knows it’s not going to go away as long as over-the-air radio can be received in large areas where data streams cannot. It’s an open question, however, whether broadcasters will want to continue spending many thousands of dollars every month on transmitters of signals that can no longer be justified financially.
One big question for radio is the same one that faces TV. That is, What will ESPN do?
ESPN is the Giant Kahuna that’s keeping millions of listeners on AM and FM radio, and viewers on cable and satellite. Many of those would leave if the same content were streamed directly over the Net. But for now ESPN appears to be fine with distributing its programming through cable and local radio. But at some point ESPN will go direct — over the Net —and avoid the old distribution methods — especially if listeners and viewers would rather have it that way.
To do that they’ll be distributing mostly through ISPs, which these days are mostly cable and phone companies. While those companies like to say they favor “neutrality” toward content, their business ideal is monopsony toward content suppliers and monopoly toward customers. So expect a lot of theater in the next couple of years.
Devoutly to be avoided is further movement toward the “fully licensed world” I warned about, two posts back. (Interesting that ESPN and others want Arbitron to do “cross-platform measurement”, even as it continues to help make the case for AM and FM radio.)
Regardless of how that goes, AM and FM are stuck in a tunnel, facing the headlights of a content distribution train that they need to embrace before it’s too late.

Leave a Reply