It’s easy to get caught up in news that WhatsApp is starting to accept advertising (after they said they would never do that), and miss the deeper point of what’s really going on: Facebook setting up a new bot-based channel through which companies and customers can communicate. Like this:

The word balloon is Facebook Messenger. But it could be WhatsApp too. From a VRM perspective, what matters is whether or not “Messenger bots” work as VRM tools, meaning they obey the individual user’s commands (and not just those of Facebook’s corporate customers). We don’t know yet. Hence the question mark.
But before we get to exploring the possibilities here (which could be immense), we need to visit and dismiss the main distractions.
Those start with Why we don’t sell ads, posted on the WhatsApp blog on 18 June 2012. Here are the money grafs from that one:
We knew we could do what most people aim to do every day: avoid ads.
No one wakes up excited to see more advertising, no one goes to sleep thinking about the ads they’ll see tomorrow. We know people go to sleep excited about who they chatted with that day (and disappointed about who they didn’t). We want WhatsApp to be the product that keeps you awake… and that you reach for in the morning. No one jumps up from a nap and runs to see an advertisement.Advertising isn’t just the disruption of aesthetics, the insults to your intelligence and the interruption of your train of thought. At every company that sells ads, a significant portion of their engineering team spends their day tuning data mining, writing better code to collect all your personal data, upgrading the servers that hold all the data and making sure it’s all being logged and collated and sliced and packaged and shipped out… And at the end of the day the result of it all is a slightly different advertising banner in your browser or on your mobile screen.
Remember, when advertising is involved you the user are the product.
Great stuff. But that was then and this is now. In WhatsApp’s latest post, Looking Ahead for WhatsApp (25 August), we have the about-face:
But by coordinating more with Facebook, we’ll be able to do things like track basic metrics about how often people use our services and better fight spam on WhatsApp. And by connecting your phone number with Facebook’s systems, Facebook can offer better friend suggestions and show you more relevant ads if you have an account with them. For example, you might see an ad from a company you already work with, rather than one from someone you’ve never heard of. You can learn more, including how to control the use of your data, here.
Pretty yucky, huh?
Earlier in the same post, however, WhatsApp says,
we want to explore ways for you to communicate with businesses that matter to you too
Interesting: Mark Zuckerberg said the same thing when he introduced messenger bots, back in April. In the video at that link, Zuck said,
Now that Messenger has scaled, we’re starting to develop ecosystems around it. And the first thing we’re doing is exploring how you can all communicate with businesses.
You probably interact with dozens of businesses every day. And some of them are probably really meaningful to you. But I’ve never met anyone who likes calling a business. And no one wants to have to install a new app for every service or business they want to interact with. So we think there’s gotta be a better way to do this.
We think you should be able to message a business the same way you message a friend. You should get a quick response, and it shouldn’t take your full attention, like a phone call would. And you shouldn’t have to install a new app.
Note the similarities in the set-up:
- Zuck: “how you can all communicate with business.”
- WhatsApp: “explore ways for you to communicate with businesses.”
This is, or should be, pure VRM: a way for a customer to issue a service request, or to intentcast for bids on a new washing machine or a car. In other words, what they seem to be talking about here is a new communication channel between customers and businesses that can relieve the typical pains of being a customer while also opening the floodgates of demand notifying supply when it’s ready to buy. Back to Zuck:
So today we’re launching Messenger Platform. So you can build bots for Messenger.
By “you” Zuck means the developers he was addressing that day. I assume these were developers working for businesses that avoid customer contact and would rather have robots take over everything possible, because that’s the norm these days. But I could be wrong. He continues,
And it’s a simple platform, powered by artificial intelligence, so you can build natural language services to communicate directly with people. So let’s take a look.
CNN, for example, is going to be able to send you a daily digest of stories, right into messenger. And the more you use it, the more personalized it will get. And if you want to learn more about a specific topic, say a Supreme Court nomination or the zika virus, you just send a message and it will send you that information.
The antecedents of “you” move around here. Could be he’s misdirecting attention away from surveillance. Can’t tell. But it is clear that he’s looking past advertising alone as a way to make money.
Back to the WhatsApp post:
Whether it’s hearing from your bank about a potentially fraudulent transaction, or getting notified by an airline about a delayed flight, many of us get this information elsewhere, including in text messages and phone calls.
This also echoes what Zuck said in April. In both cases it’s about companies communicating with you, not about you communicating with companies. Would bots work both ways?
In “‘Bot’ is the wrong name…and why people who think it’s silly are wrong”, Aaron Batalion says all kinds of functionality now found only in apps will move to bots—Messenger’s in particular. “In a micro app world, you build one experience on the Facebook platform and reach 1B people.”
How about building a one-experience bot so 1B people can reach businesses the same way?
Imagine, for example, that you can notify every company you deal with that your last name has changed, or you’ve replaced a credit card. It would be great to do that in one move. It would also be VRM 101. But, almost ten years into our project, nobody has built that yet. Is Facebook doing it?
Frankly, I hope not, because I don’t want to see VRM trapped inside a giant silo.
That’s why I just put up Market intelligence that flows both ways, over in Medium. (It’s a much-updated version of a post I put up here several years ago.)
In that post I describe a much better approach, based on open source code, that doesn’t require locating your soul inside a large company for which, as WhatsApp put it four years ago, you’re the product.
Here’s a diagram that shows how one person (myself, in this case) can relate to a company whose moccasins he owns:

The moccasins have their own pico: a cloud on the Net for a thing in the physical world. For VRM and CRM purposes, this one is a relationship conduit between customer and company.
A pico of this type comes in to being when the customer assigns the QR code to the moccasins and scans it. The customer and company can then share records about the product, or notify the other party when there’s a problem, a bargain on a new pair, or whatever. It’s tabula rasa: wide open.
The current code for this is called Wrangler. It’s open source and in Github. For the curious, Phil Windley explains how picos work in Reactive Programming With Picos.
I’ll continue on this theme in the next post. Meanwhile, my main purpose with this one is to borrow interest in where Facebook is going (if I’m guessing right) with Messenger bots, and do it one better in the open and un-silo’d world, while we still have one to hack.
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save

 This is a shopping vs. advertising story that starts with the JBP Flip 2 portable speaker I bought last year, when Radio Shack was going bankrupt and unloading gear in “Everything Must Go!” sales. I got it half-off for $50, choosing it over competing units on the same half-bare shelves, mostly because of the JBL name, which I’ve respected for decades. Before that I’d never even listened to one.
This is a shopping vs. advertising story that starts with the JBP Flip 2 portable speaker I bought last year, when Radio Shack was going bankrupt and unloading gear in “Everything Must Go!” sales. I got it half-off for $50, choosing it over competing units on the same half-bare shelves, mostly because of the JBL name, which I’ve respected for decades. Before that I’d never even listened to one.
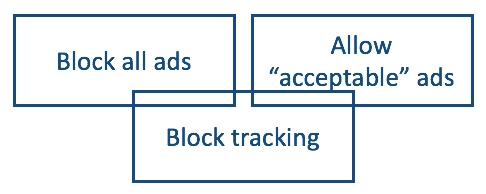
 The program is called
The program is called 


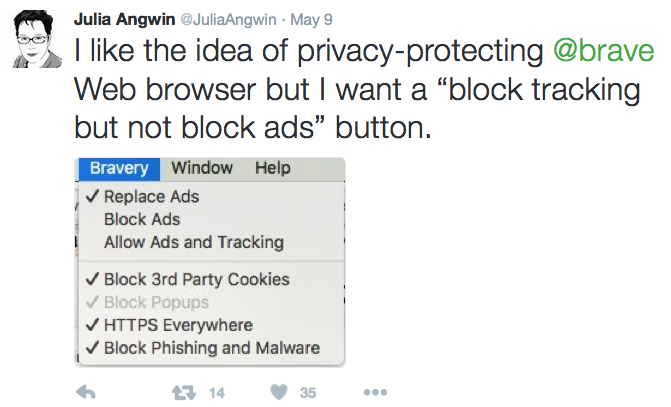

 I’m serious.
I’m serious.